Configuration Managment¶
Table of Contents
This chapter will detail how to back-up, restore and reset to defaults of your system configuration.
Configuration Backup¶
Web GUI
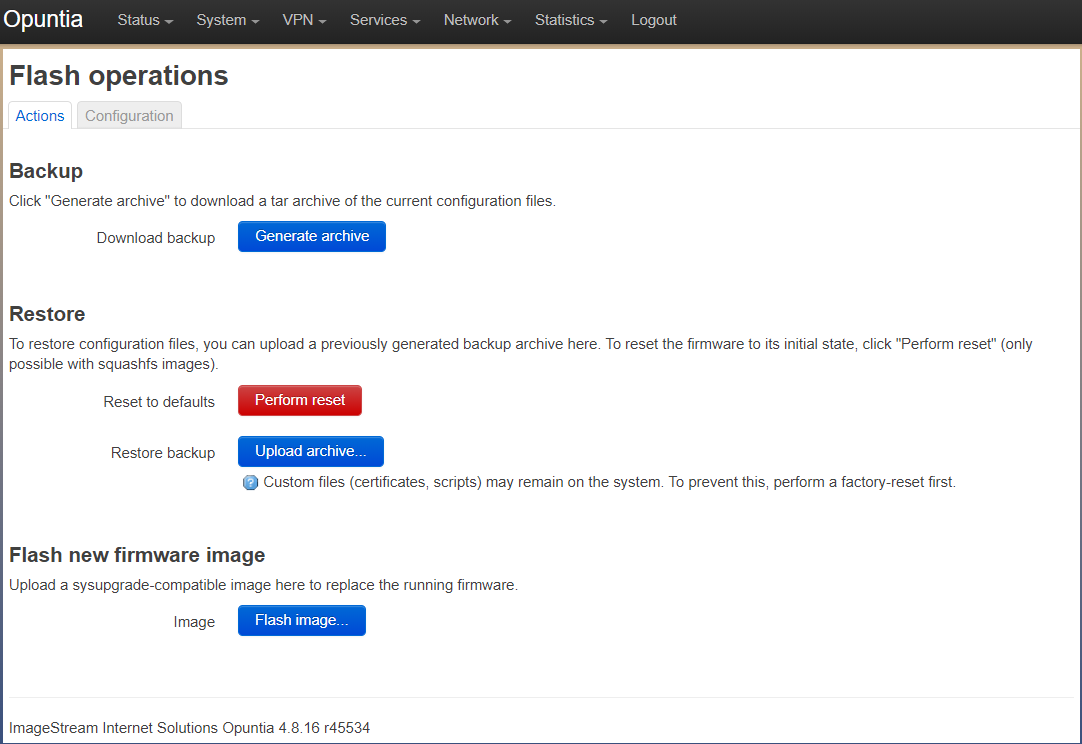
The easiest wasy to get a backup of an Opuntia system is to use the Backup option on the “Flash operations” page.
Main Menu - System –> Backup/Flash Firmware
To get a backup; simply click the “Generate archive” button. This will cause the system to generate a backup file using the following format. “backup-<Current hostname>-<Current Date>.tar.gz”. This file will be downloaded by your Web Browser.
CLI
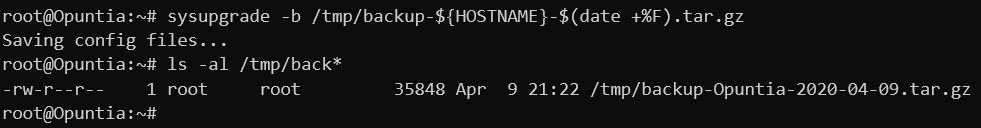
The process to backup using the CLI is more involved, you first must manually generate the backup file. And then transfer the file off of the system.
sysupgrade -b /tmp/backup-${HOSTNAME}-$(date +%F).tar.gz
This will generate a backup file that matches the same format you get when using the Web GUI method. But it is possible to use whatever filename you wish.
Important
If you do generate a backup file make sure you use the /tmp/ directory as the destination.
Once you have created a backup image you must transfer it off of the system. The simplest way to do this is to use the “scp” command. This allows you to transfer the image off of the system and to a remote host.
Restoring Configurations¶
Web GUI
To restore the system from a downloaded configuration file, first navigate to the “Flash operations” page.
Main Menu - System –> Backup/Flash Firmware

There are two options for restoring the system. You can restore from a saved backup file or you can restore the system to the default configuration. We will cover both operations in this section.
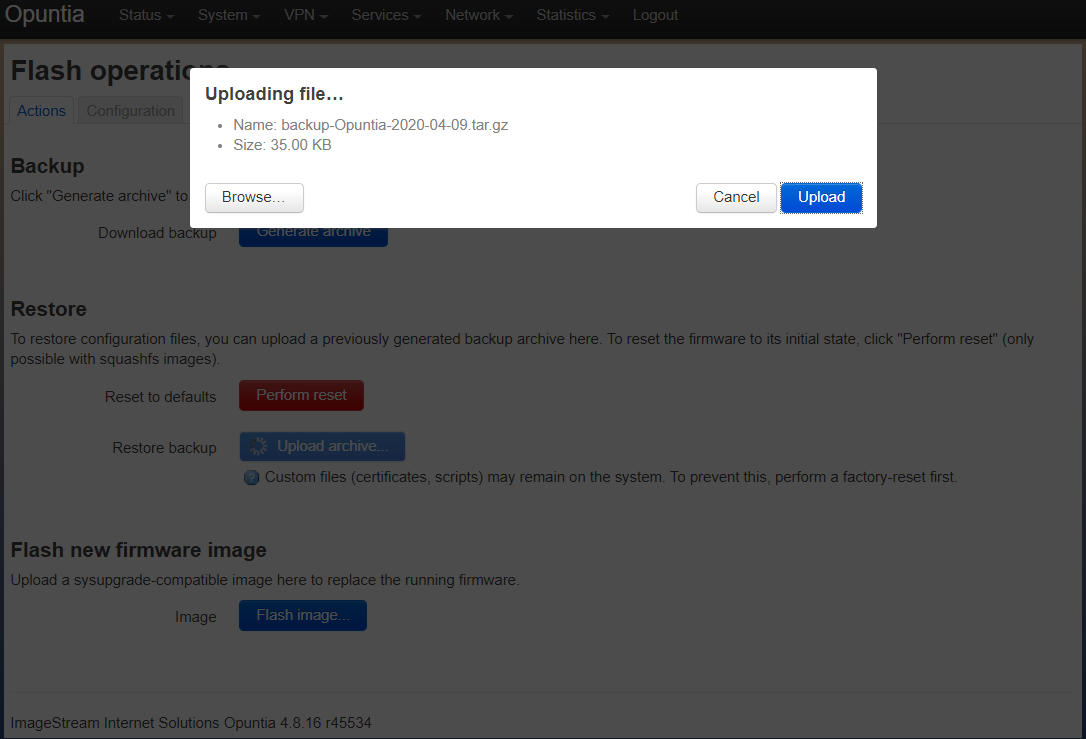
To restore from a saved backup; you begin by first uploading the backup file to the Opuntia system. This is done by clicking the “Upload archive” button. This brings up a local file browser. You need to select your desired backup file. Once selected you will see the following upload summary dialog box. That will show your filename and size of the configuration file. Click upload to be the upload process.
Once the backup configuration file is uploaded, you will see a detailed list of all of the files contained in the backup configuration file. You will need to scroll to the bottom of the list to see the contine button.
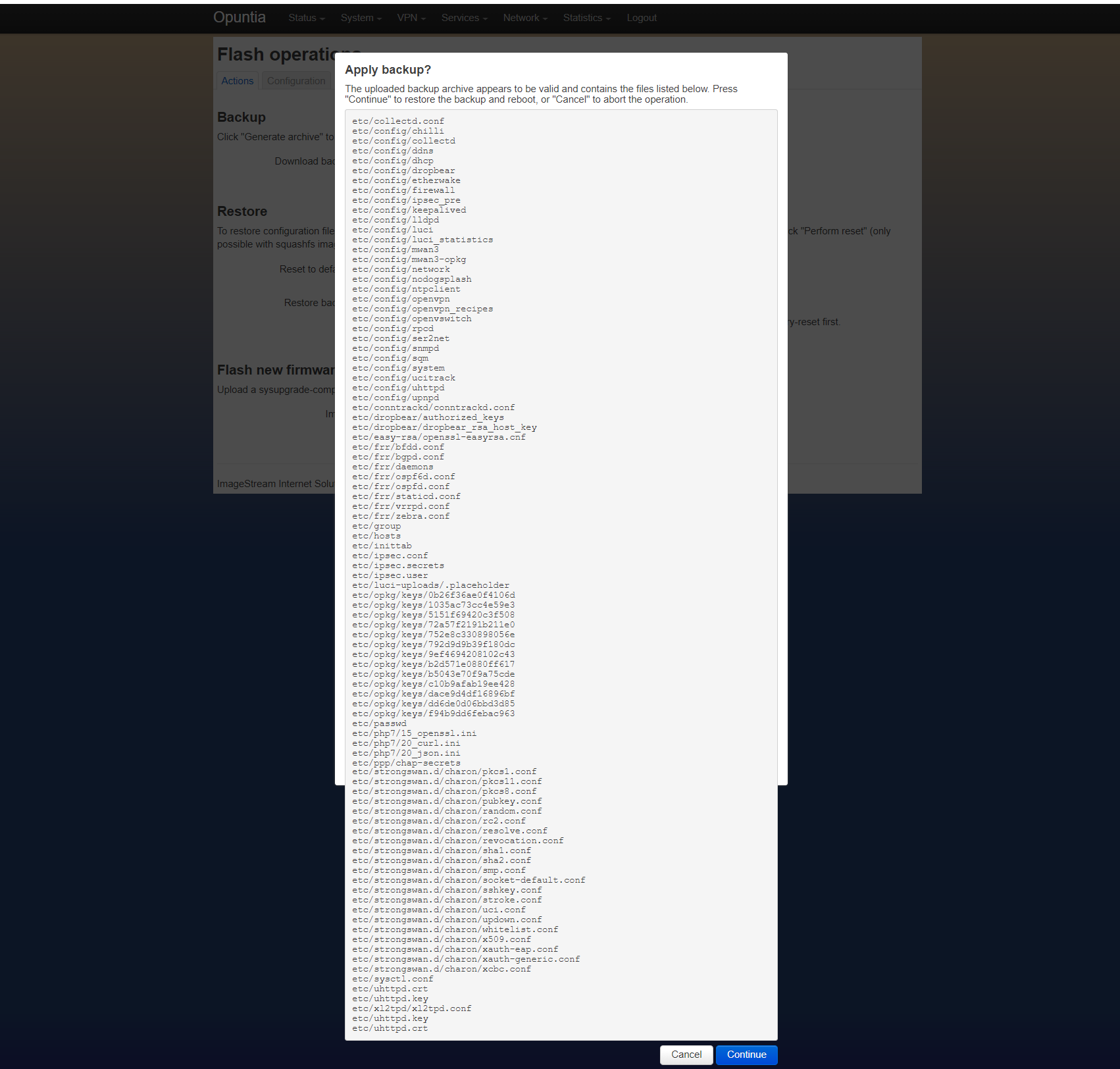
Once the contiue button is pressed the system will reboot. If the URL does not change, the Web GUI will reconnect after the reboot process is complete.
Note
The configuration can change the ip address of the system so you may have to reconnect to a different url.
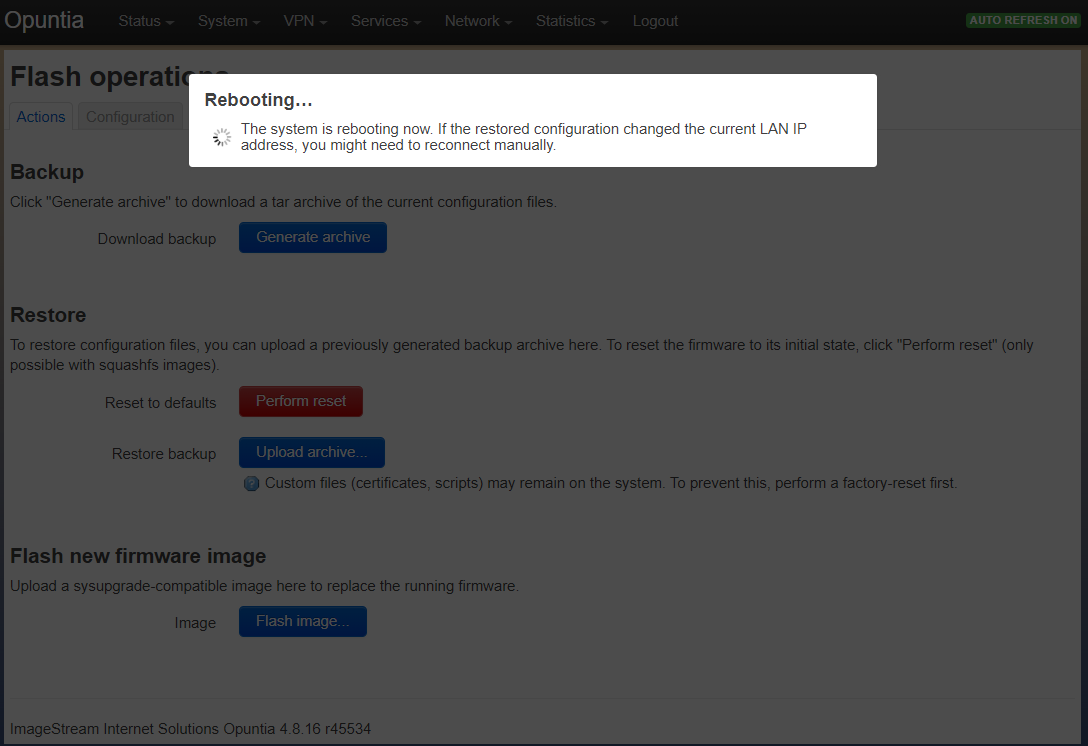
This completes restoring a saved configuration file.
To restore the system to a default state it is needed to click on the “Perform reset” button. And then to confirm that you want to restore to factory defaults. This then performs a system reboot.
CLI
To restore a saved backup configuration file using the command line interface you must first upload the file to the system. The recommended method is to use “scp” to upload the file.
Important
If you are manual uploading configuration files to a system you must use the /tmp directory as the destination for the file.
Covering all the options of the scp command is beyond the scope of this manual. But this command line and example will work for most situations. This example assumes that the filename of the backup file is “backup-Opuntia-2020-04-09.tar.gz” and the Opuntia system has an ip address of 192.168.79.14
scp backup-Opuntia-2020-04-09.tar.gz root@192.168.79.14:/tmp/

To restore from the uploaded use the following command. If you do not wish to reboot immediately remove the “reboot” from the end of this example.
sysupgrade -r /tmp/backup-Opuntia-2020-04-09.tar.gz ; sync ; reboot
